The longer the period and the higher the rate, the more powerful compounding becomes. This means that 10,000 received in 5 years is equivalent to 7,128.55 today, at a 7% rate. So receiving 1,000 next year is worth less than 1,000 today—because you’re giving up the chance to earn interest. For monthly payouts, rate is divided by 12 and nper is multiplied by 12. The present value of annuity-immediate is $820 and that of annuity-due is $877.

Problem 6: Present value annual discounting

Higher discount rates and longer time horizons shrink the present value of a single amount present value. The future value tells you how much an investment made today will grow to, based on compounding at a given rate. The pmt argument is filled with the payment per period ($200 in this case, supplied as a negative figure showing outflow for Cal). The future value is disregarded here while the next argument confirms the annuity type as regular or due. 0 is mentioned in the first instance but you may leave the cell blank or skip this argument as it would default to 0 anyway.
Problem 2: Present value of a single amount
That is because as per the time value of money, payments received way ahead in the future have dwindling and very low value enough to be defined in the present. To be converted into a monthly interest rate, 7% will be divided by 12 (as done in the first argument where C3/C4). Also, the number of periods in 3 years with monthly compounding will be 3 times 12 (reflected in the second argument). Cashflow is a measure of a company’s financial performance over a specific period of time. The present value of a single amount is the value today of a future payment. At 12% interest per year compounded semi-annually, the company needs to invest $334,000 today to accumulate $600,000 in 5 years.
Calculations by Function
- A perpetuity is an annuity in which the constant periodic payments continue indefinitely.
- The present value of $10,000 will grow to a future value of $10,824 (rounded) at the end of one year when the 8% annual interest rate is compounded quarterly.
- Also see annuity due, annuity in advance, annuity in arrears, and ordinary annuity.
- Because the PV of 1 table had the factors rounded to three decimal places, the answer ($85.70) differs slightly from the amount calculated using the PV formula ($85.73).
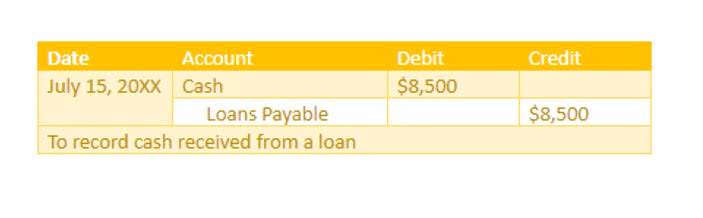
- Let’s have a show of the Excel effects of this cash flow with the following case example.
- An ordinary annuity has end-of-the-period payments while annuity-due has beginning-of-the-period payments.
Our explanation of future value will use timelines for each of the many illustrations in order for you to develop a thorough understanding of the future value of a single amount. Throughout our explanation we will utilize future value tables and future value factors. After mastering these calculations of the future value of a single amount, you are encouraged to use a financial calculator or computer software in order to obtain more precision. The present value of an amount refers to today’s value of the amount to be received at a point of time in future.
Account #2: Semiannual Compounding
We see that the present value of receiving $5,000 three years from today is approximately $3,940.00 if the time value of money is 8% per year, compounded quarterly. Behind every table, calculator, and piece of software, are the mathematical formulas needed to compute present value amounts, interest rates, the number of periods, and the future value amounts. We will, at the outset, show you several examples of how to use the present value formula in addition to using the PV tables. If there are two or more future amounts occurring at different times for an investment, their present value can be determined by simply discounting each amount separately. For example, if an amount of $5,000 occurs at the end of two gym bookkeeping years, and a second amount of $6,000 occurs at the end of five years, you simply calculate the present value of each and combine them. In the illustrations of the present value of 1 (shown earlier) we assumed that interest was compounded on an annual basis.
- They allow you to assess whether future cash flows meet your required return.
- Once you know these three variables, you can plug them into the appropriate equation.
- The following timelines will allow us to visualize the compounding of interest and its effect on each account’s ending balance.
- You want to know the value of your investment now to acheive this or, the present value of your investment account.
Because interest is compounded quarterly, we convert 2 years to 8 quarters, and the annual rate of 8% to the quarterly rate of 2%. The present value of $10,000 will be earning compounded interest every three months. During the first quarter, the account will earn $200 ($10,000 x 2%; or $10,000 x 8% x 3/12 of a year) and will result in a balance of $10,200 on March 31. During the second quarter of 2025 the account will earn interest of $204 based on the https://antar88.co/period-costs-definition-example-vs-product-costs/ account balance as of March 31, 2025 ($10,200 x 2% per quarter). The interest for the third quarter is $208 ($10,404 x 2%) and the interest for the fourth quarter is $212 ($10,612 x 2%).
Calculating the Future Value of a Single Amount (FV)

Of course, both calculations could be proved wrong if you choose the wrong estimate for your rate of return. Present value, an estimate of the current value of a future sum of money, is calculated by investors to compare the probable benefits of various investment choices. For example, instead of paying $100 cash a person is allowed to pay $9 per month for 12 months. The interest rate is not stated, but the implicit rate can be determined by use of present value factors.
